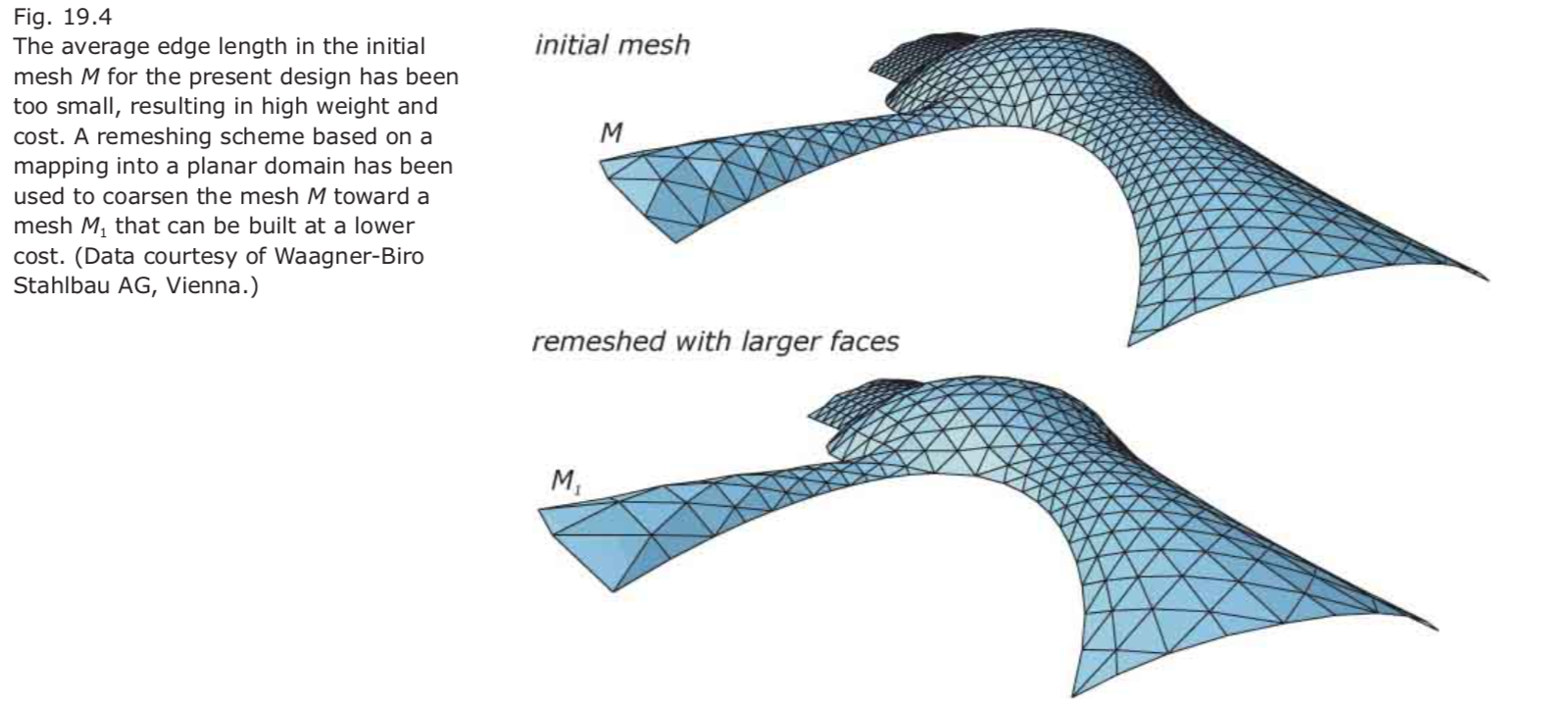
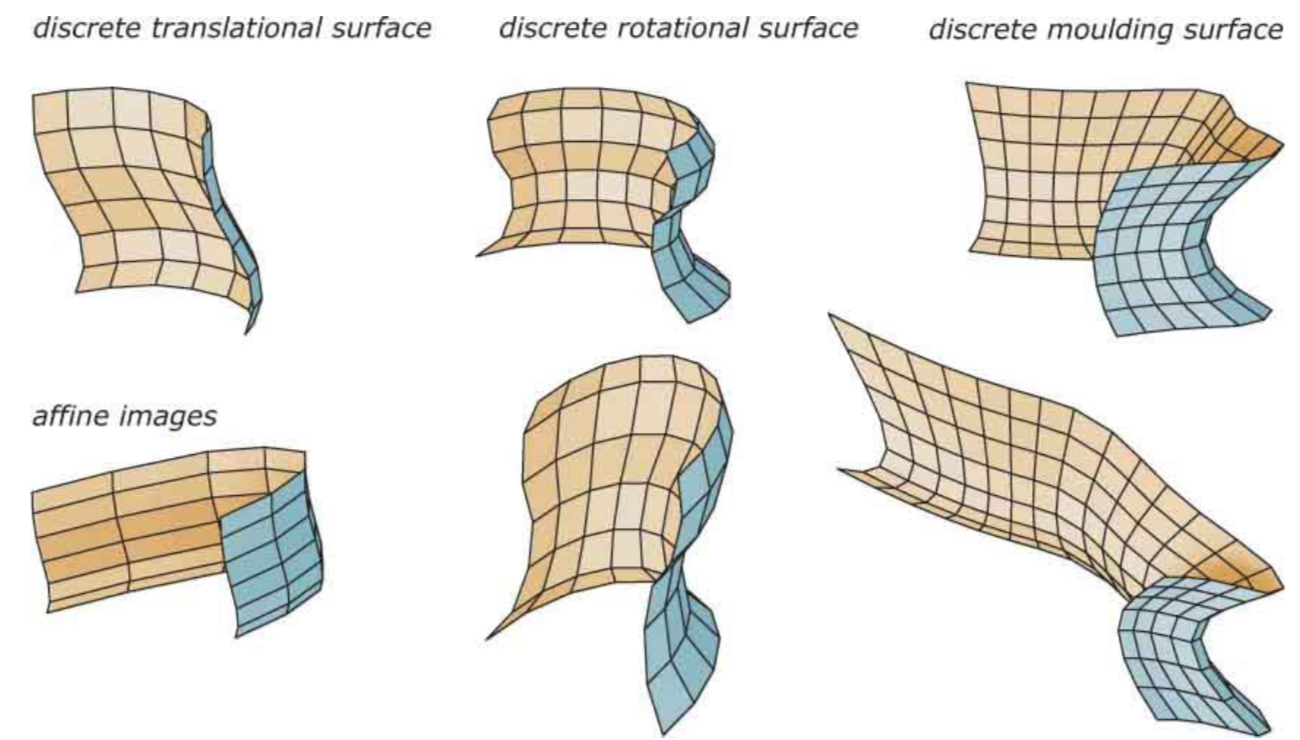
Discrete freeform structure

Triangle meshes 三角网格
Aesthetics is greatly enhanced if the mesh can be decomposed into three families of fair polygons (structure lines).
- six beams meeting in a node means a significantly higher node complexity compared to other types of meshes.
- the per-area cost of triangular glass panels is higher than that of quadrilateral panels.
- one aims at less steel, more glass, and less weight, which also points to non-triangular faces.
- triangle meshes in general torsion-free nodes do not exist.
- triangle meshes do not possess offsets at constant face-face or edge-edge distance.
Quadrilateral meshes with palnar faces 具有平面面的四边网格
- Rotational PQ mesh.
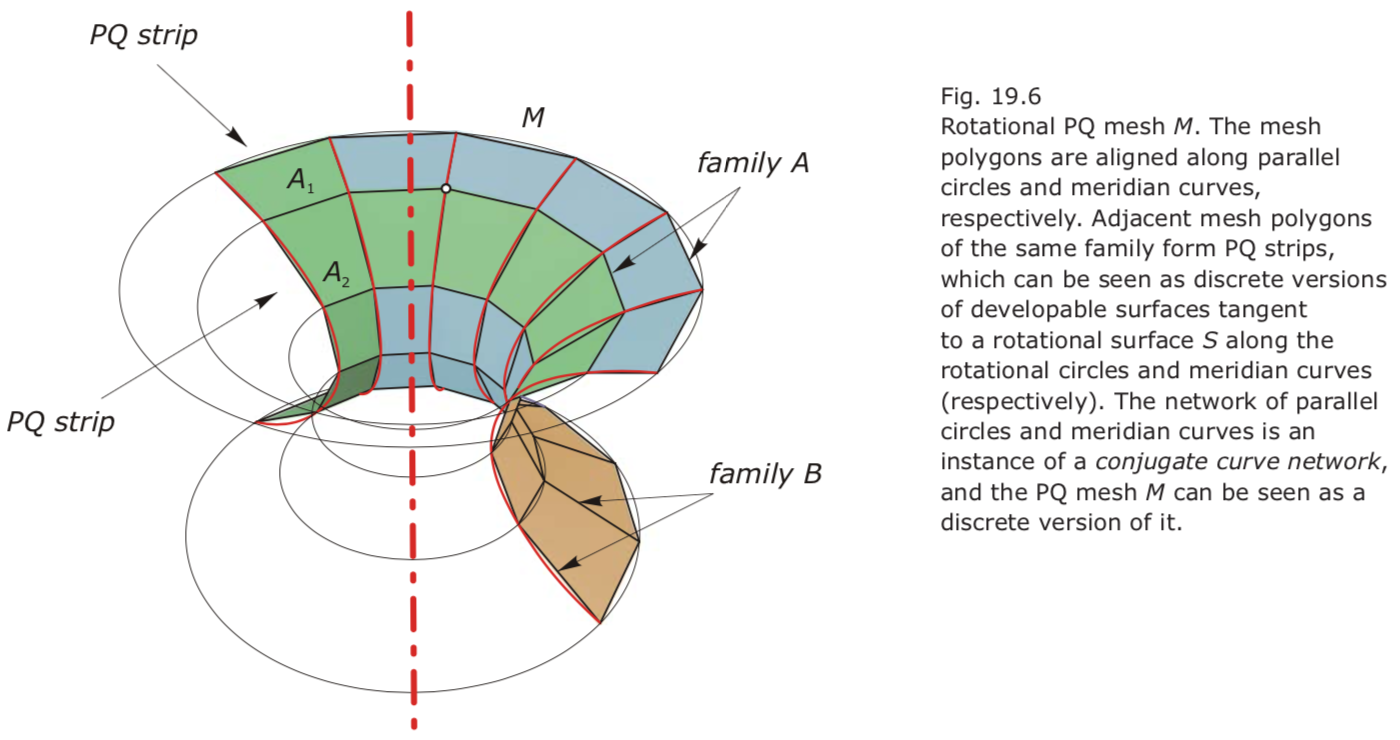
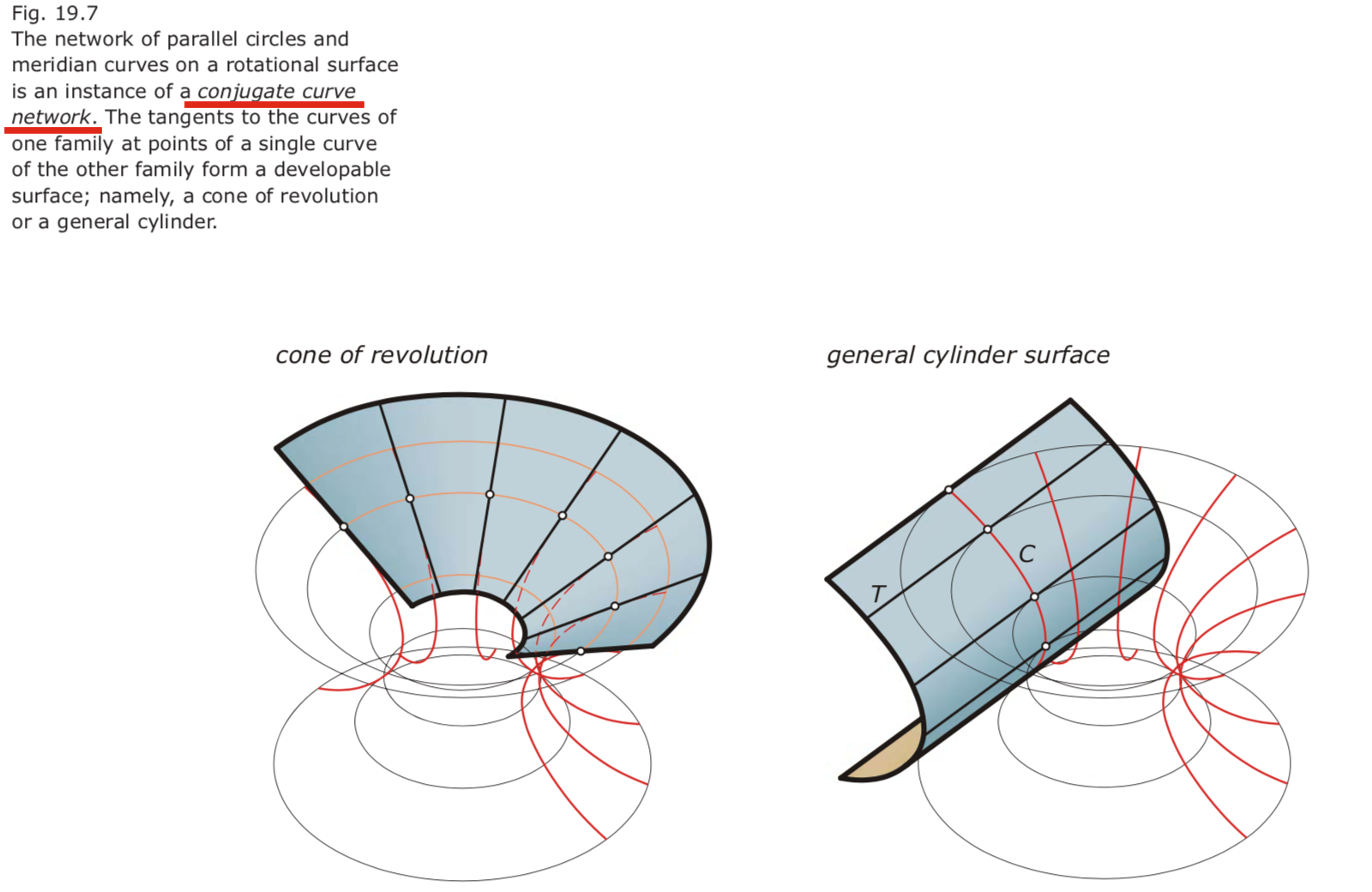
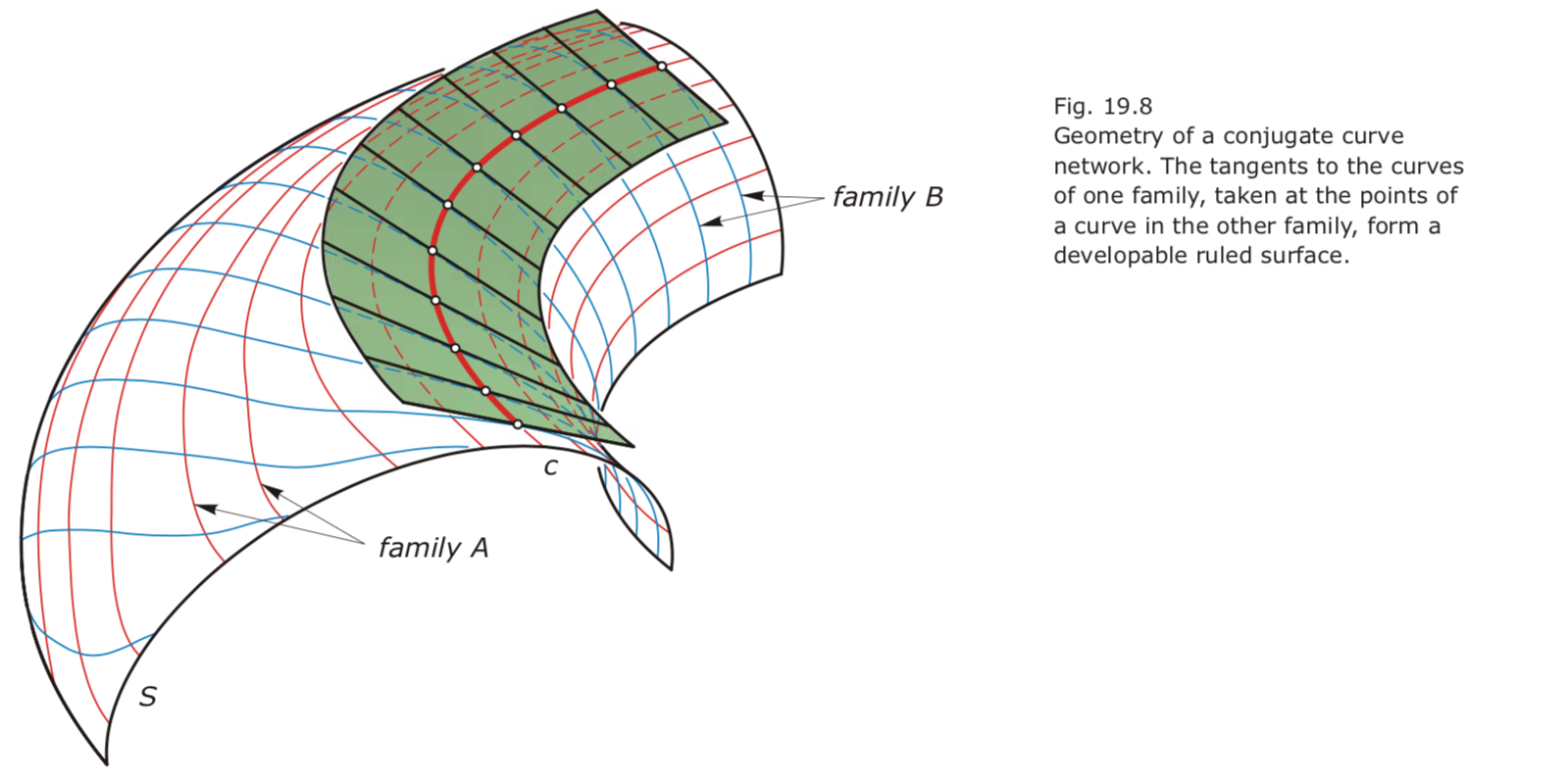
- Conjugate curve networks.
Pick a curve c in the network and compute in each of its points the tangent to the curve from the other family. Then, these tangents must form a developable ruled surface.
A network of curves resulting by translation is another simple example of a conjugate curve network.
It carries infinitely many conjugate curve networks!- Hyperbolic paraboloid.
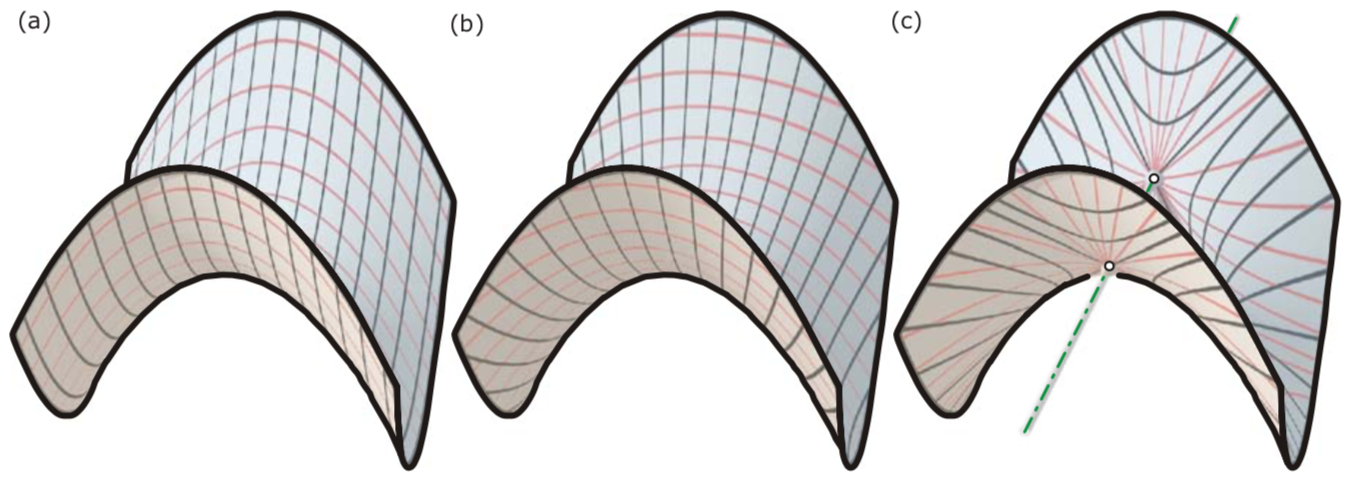
- Principal curvature lines.
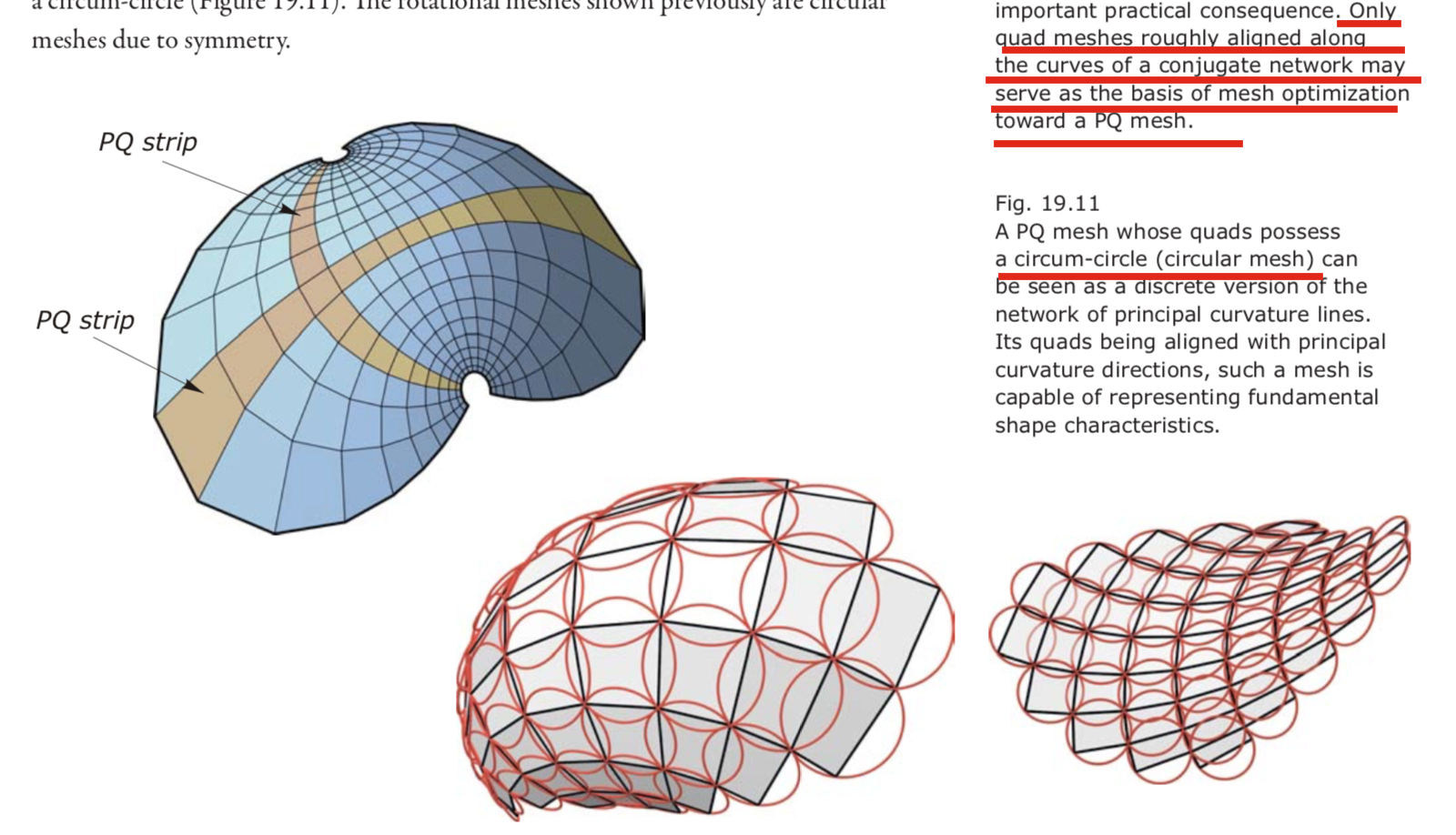
curve network that is conjugate and orthogonal.- Planar quad meshes are discrete versions of conjugate curve networks.
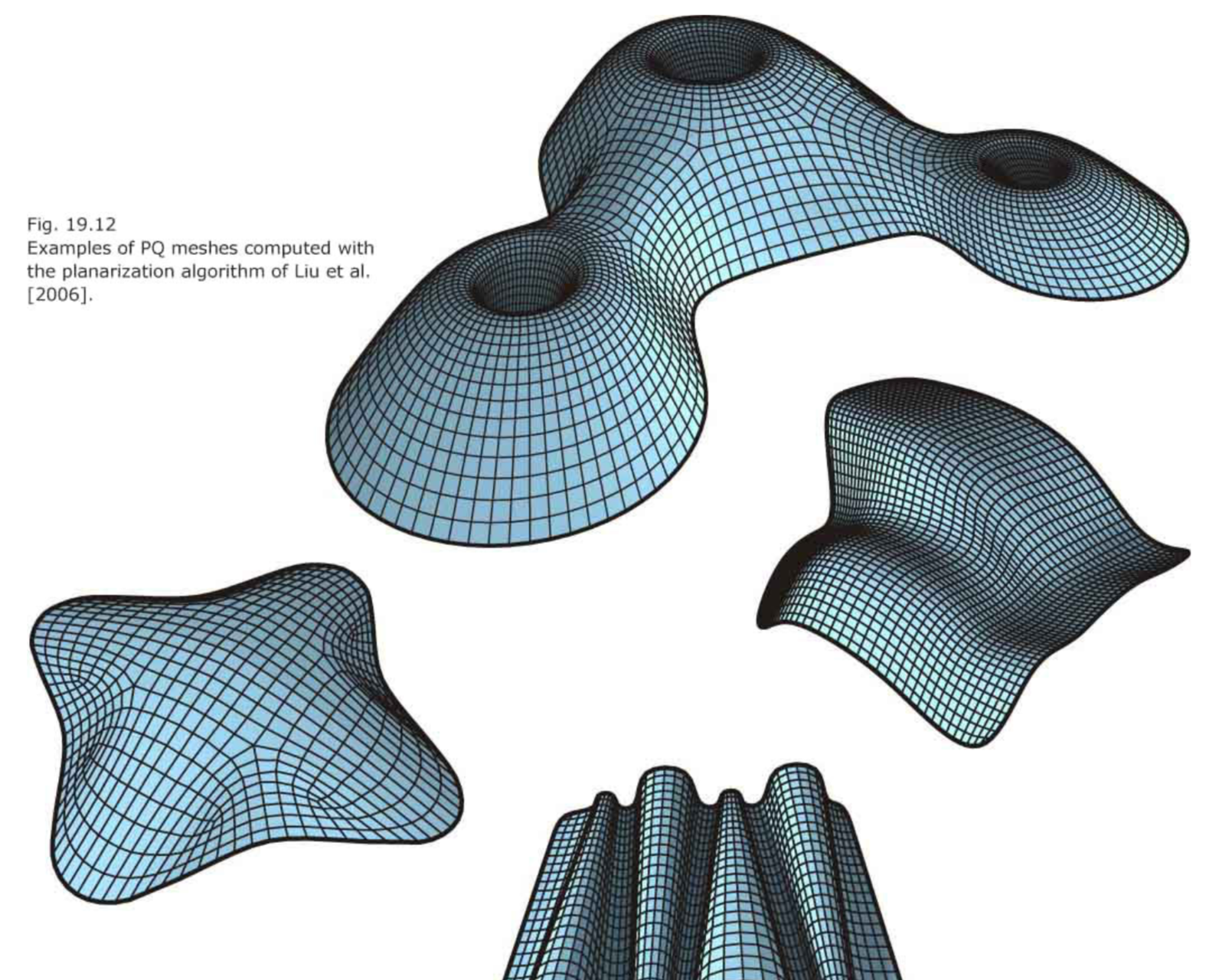
- A planarization algorithm.
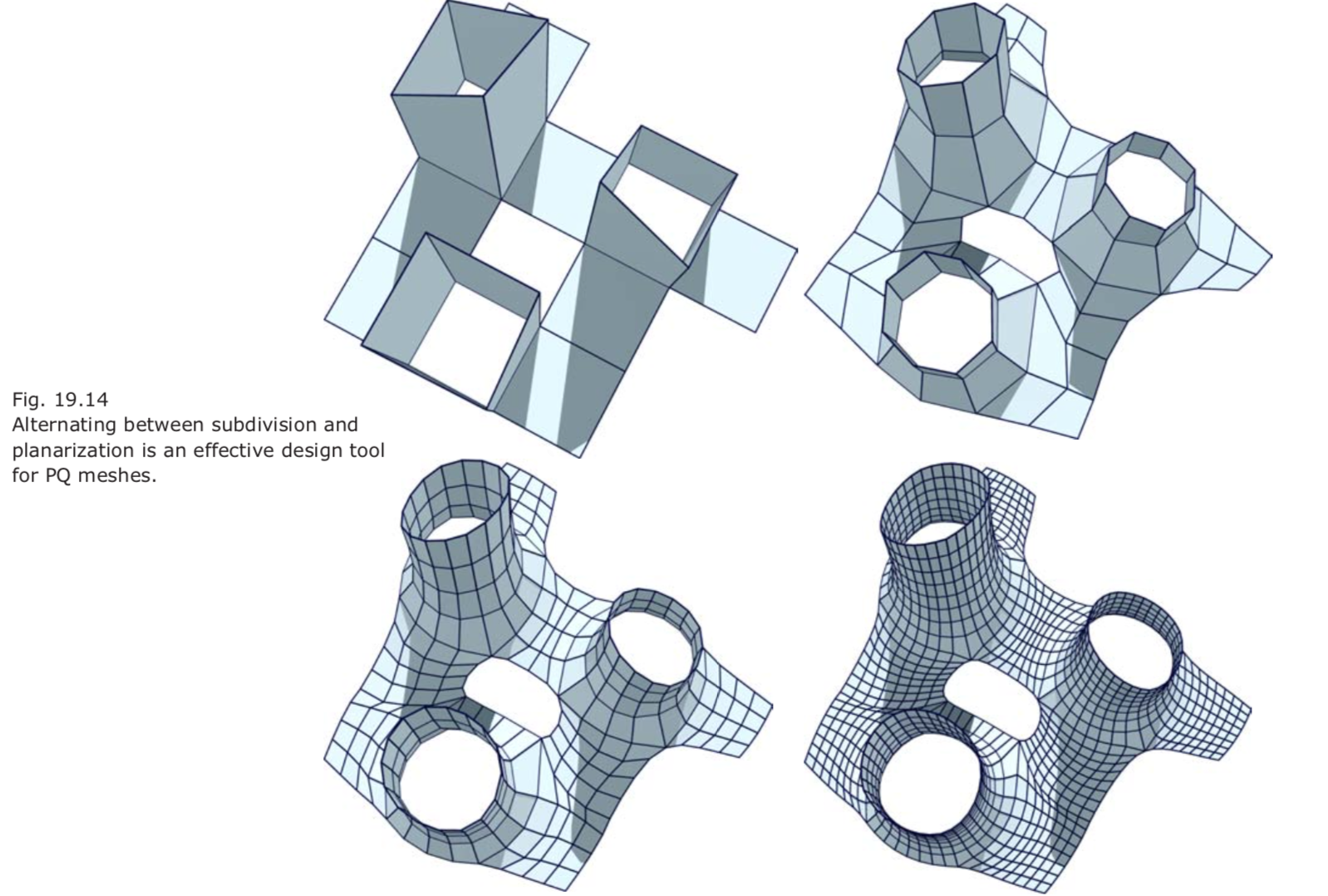
if the input mesh has been extracted from a conjugate curve network chances are high that the optimization will not get stuck in an undesirable solution and thus may yield a practically useful result- Combination of subdivision and planarization as a design tool.
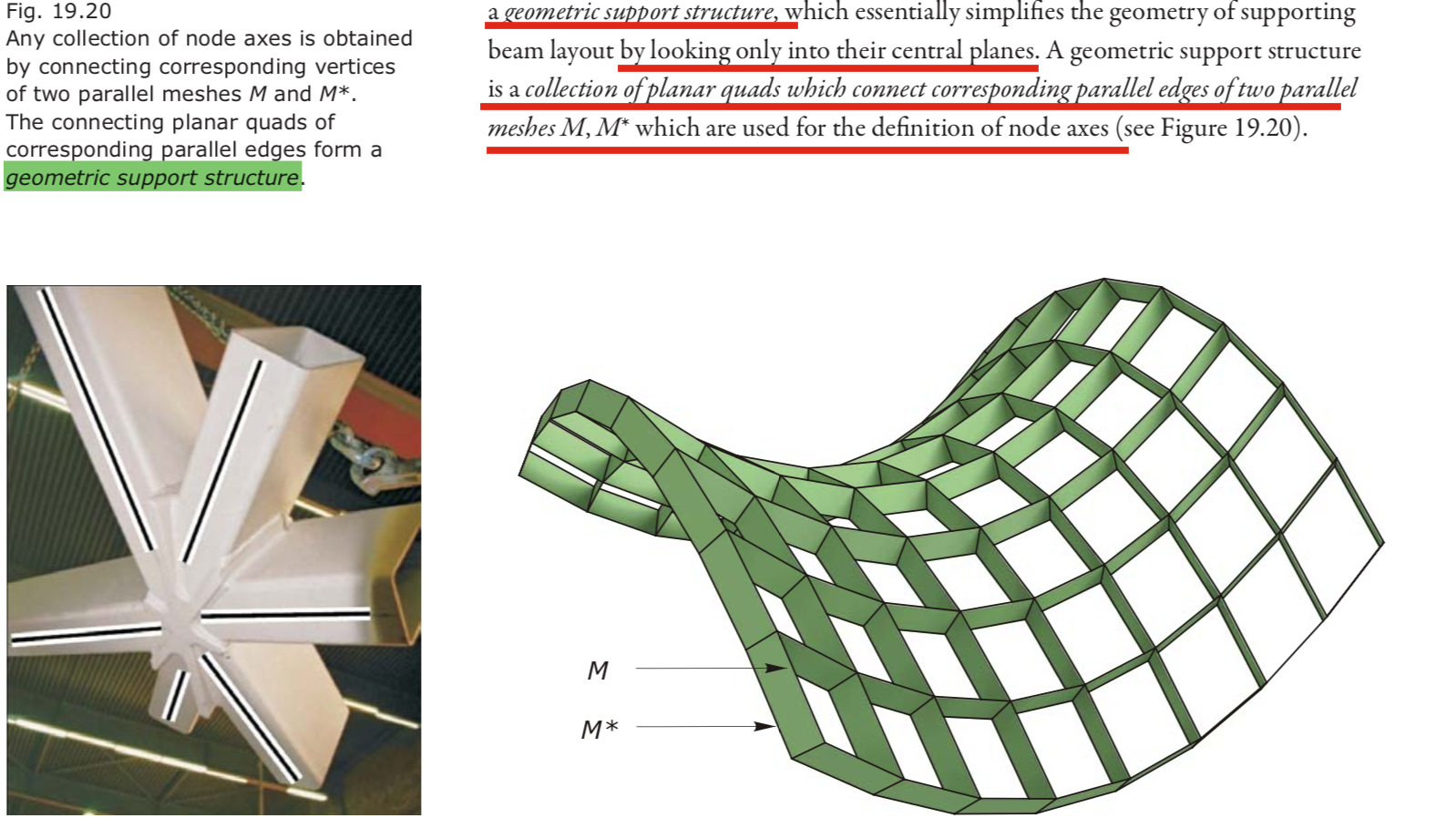
Parallel meshes, offsets, and supporting beam layout 平行网格,等距面,支撑梁柱结构
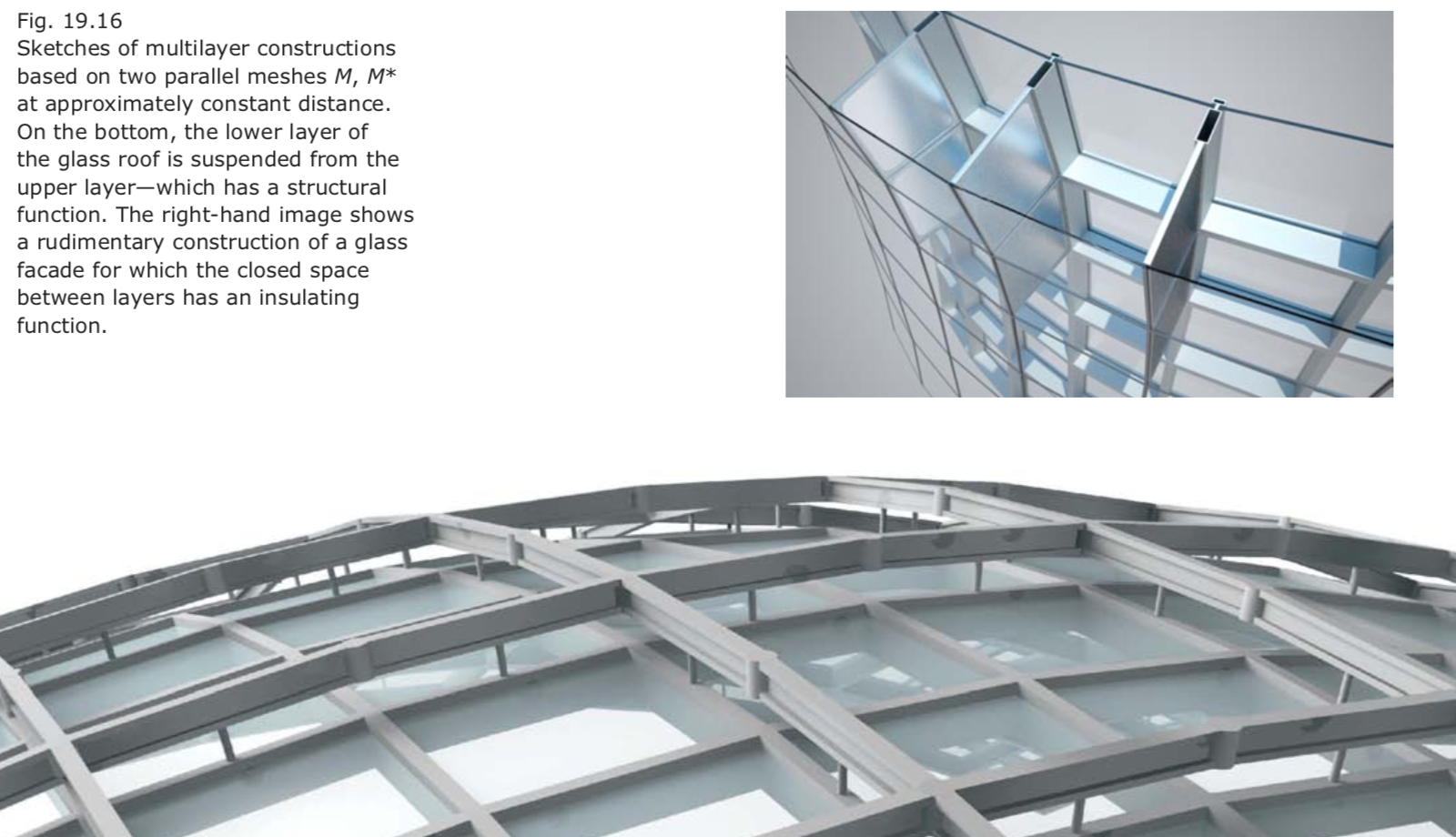
- We call two meshes M, M* parallel if there is a one-to-one correspondence among their vertices, edges, and faces (such meshes are called combinatorially equivalent) and if corresponding edges are parallel.
- any mesh parallel to a PQ mesh is also a PQ mesh.
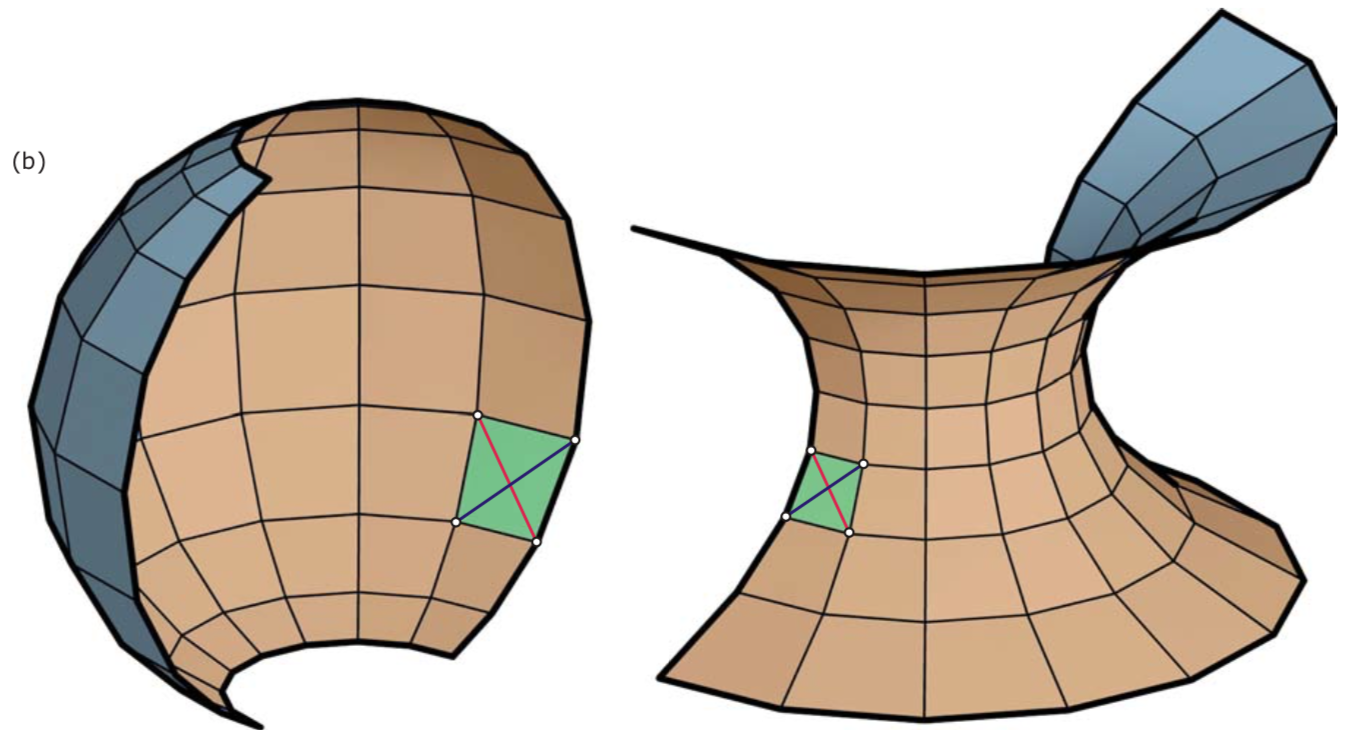
- Requiring that the node axes be roughly orthogonal to the underlying design surface implies that the mesh M has planar or spherical shape. For a general freeform triangle mesh M, there is no chance to construct a practically useful support structure with torsion-free nodes.
Offset meshes 等距网格
- Offset surfaces revisited.
Note that the normals of F are normals of F d as well
The tangent planes at corresponding points of F and F d are parallel and at constant distance d.- PQ meshes with exact offsets.
An offset mesh Md of a PQ mesh M is parallel to M and lies at constant distance d to M.- Vertex offsets: The distance of corresponding vertices of M and Md has a constant value d, which does not depend on the vertex.
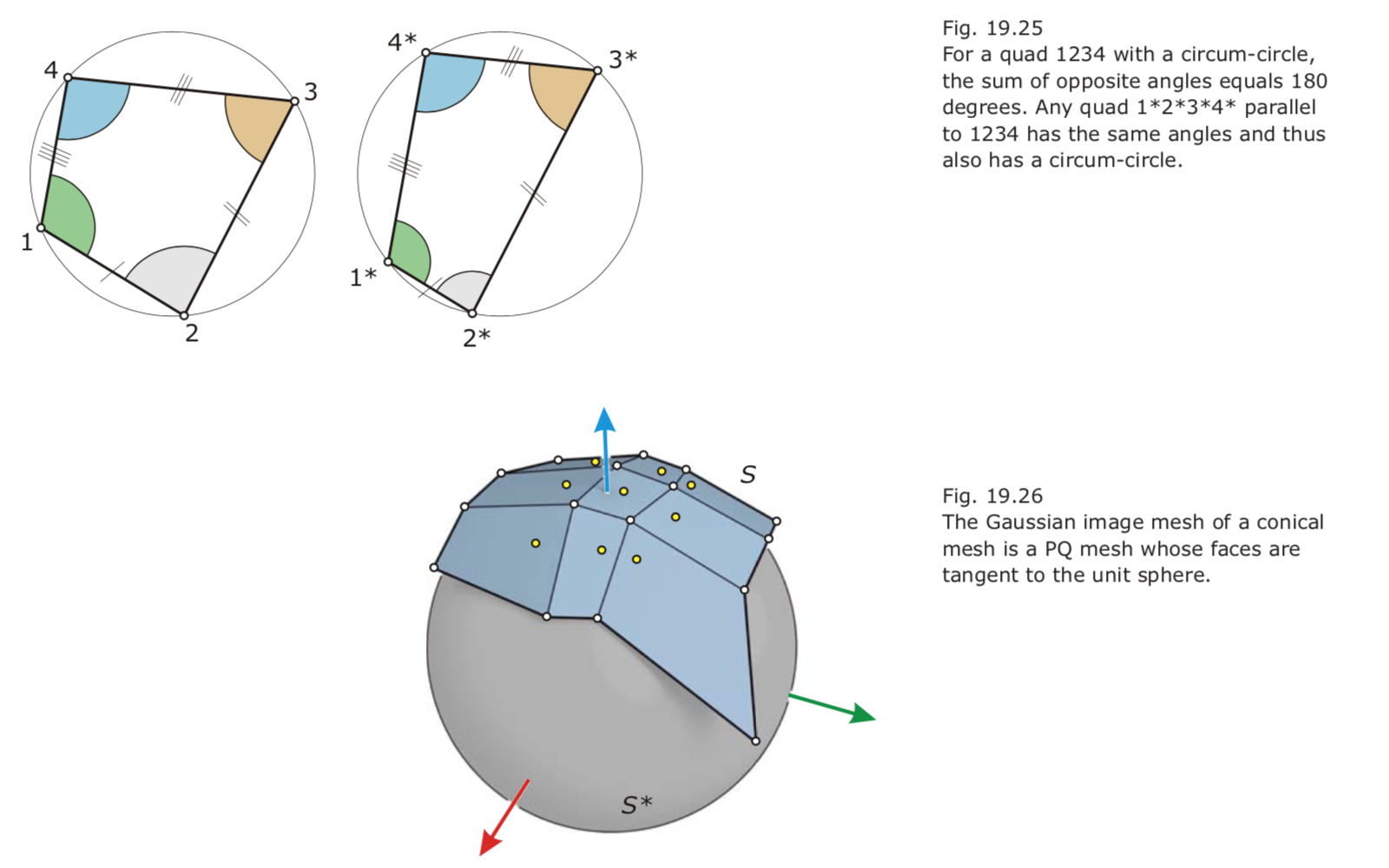
Md is a vertex offset of M if and only if the vertices of the Gaussian image mesh S are contained in the unit sphere S*. In this case, M and Md are circular meshes (i.e., each face has a circum-circle).- Edge offsets: The distance of corresponding parallel edges of M and Md (actually, lines that carry these edges) does not depend on the edge and equals d.
Md is an edge offset of M exactly if the edges of the Gaussian image mesh S are tangent to the unit sphere S*.- Face offsets: The distance of corresponding faces of M and Md (actually, the parallel planes of corresponding faces) is independent of the face and equals d.
Md is a face offset of M if and only if the faces of the Gaussian image mesh S are tangent to the unit sphere S*. In this case, M and Md are conical meshes.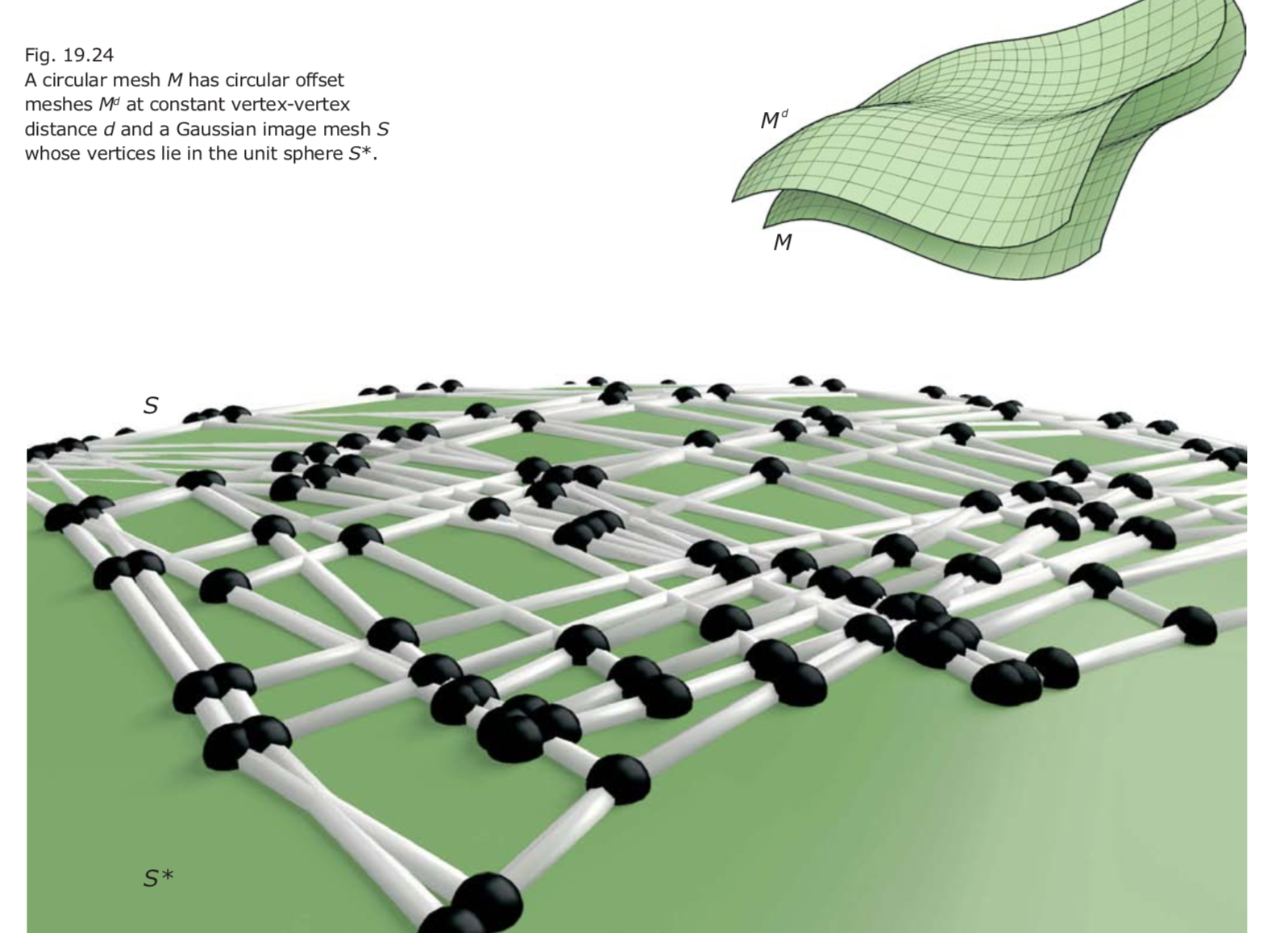
cone condition at a vertex: The sum of opposite edge angles must be equal: $ω_1 + ω_3 = ω_2 +ω_4.$
This angle balance condition may also be seen as a discrete condition for orthogonality of the two mesh polygons passing through a vertex.
Because conical meshes are orthogonal and conjugate in a discrete sense, conical meshes are a discrete version of the network of principal curvature lines on a smooth surface.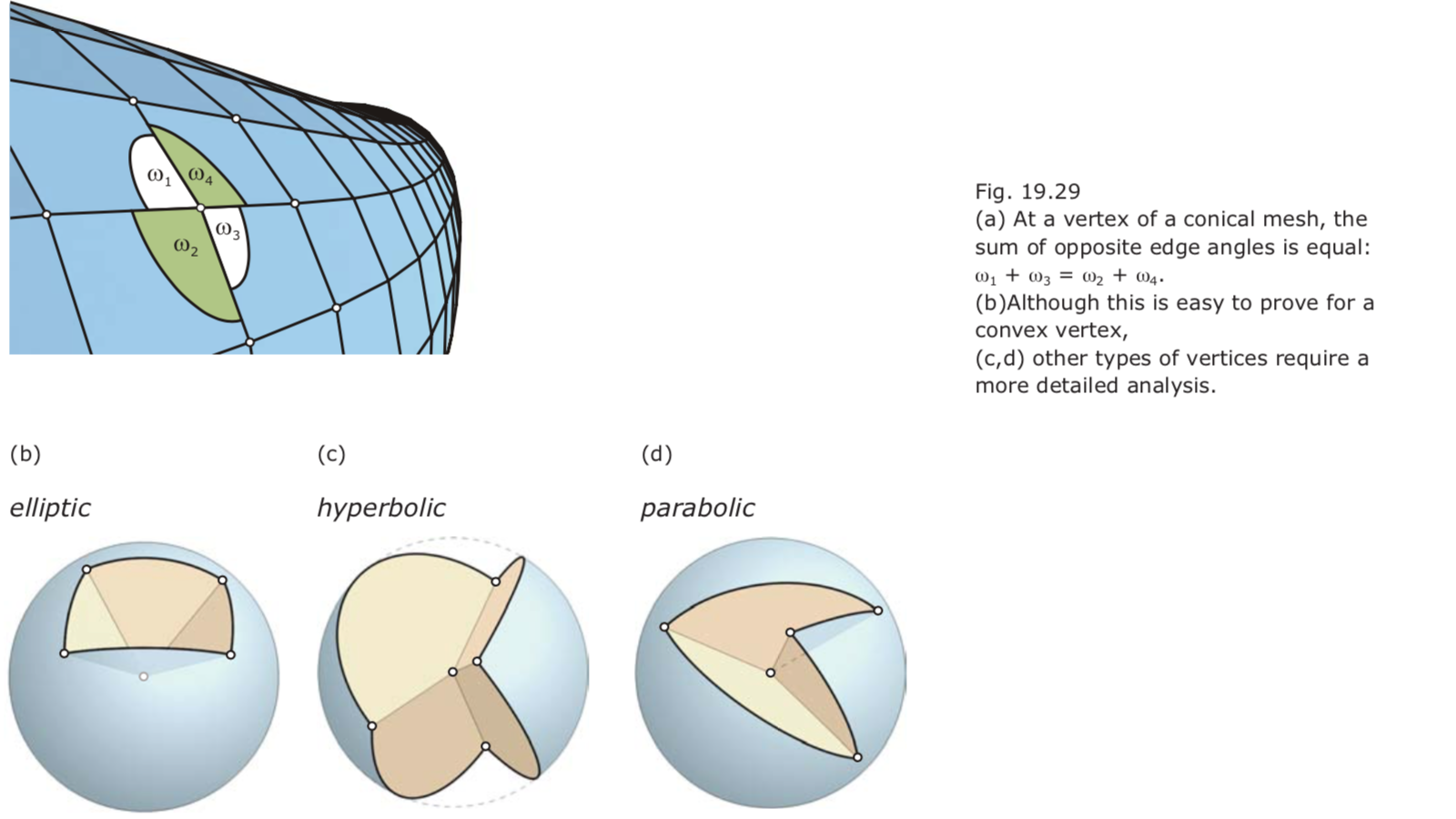
Optimal discrete surfaces 最优离散曲面
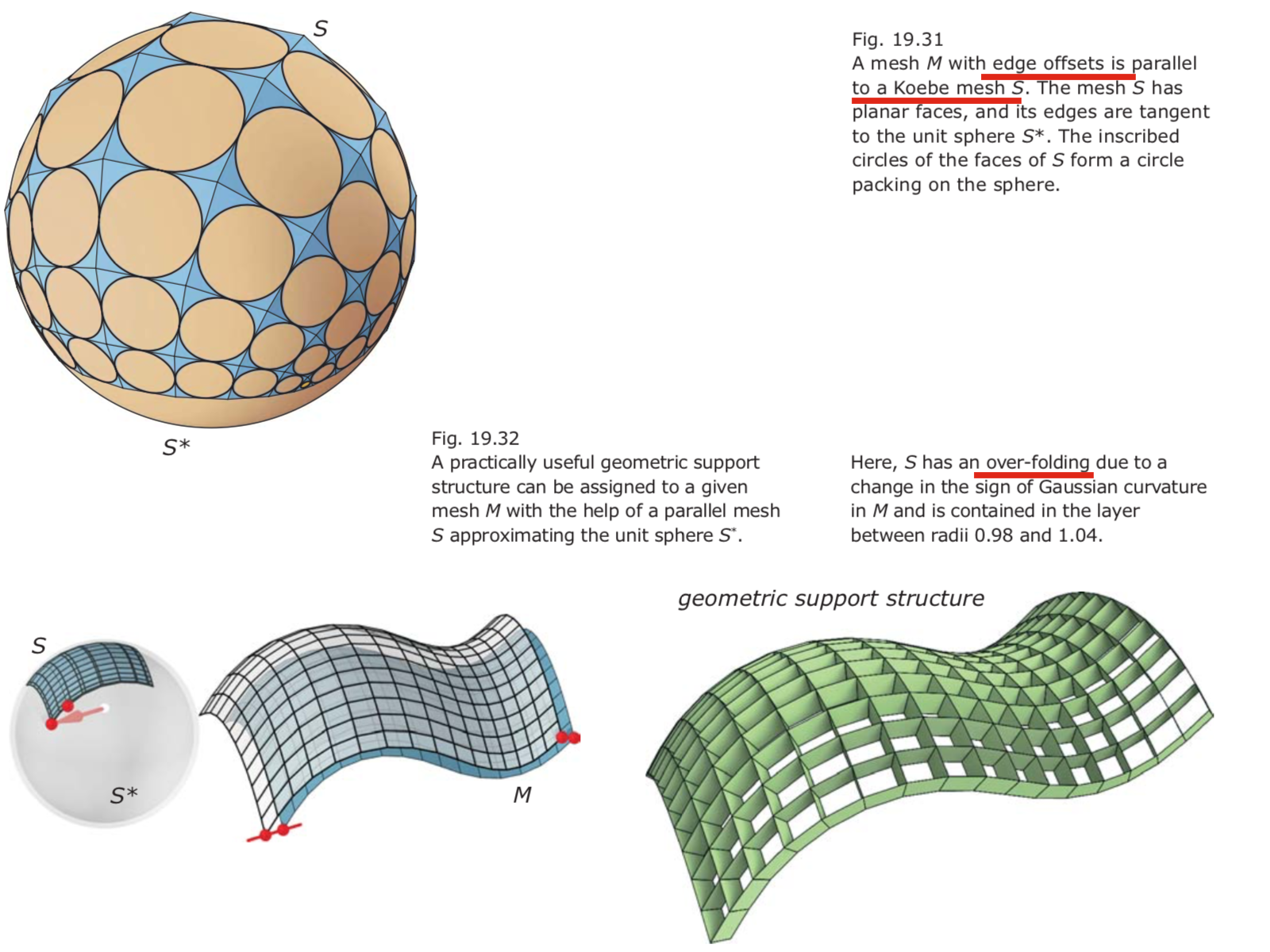
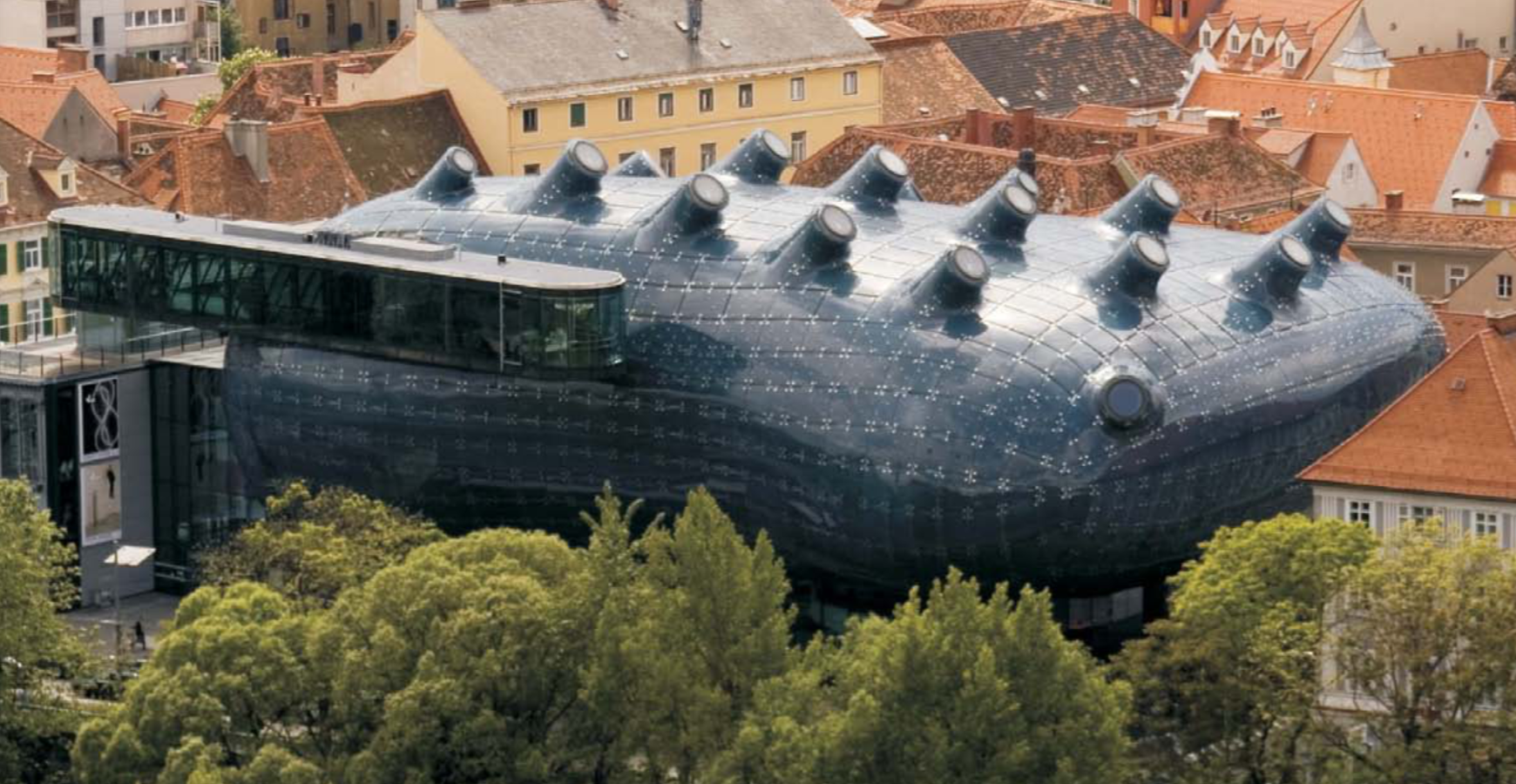
- Koebe meshes S introduced in connection with edge offsets are the basis of an elegant construction of discrete minimal surfaces.
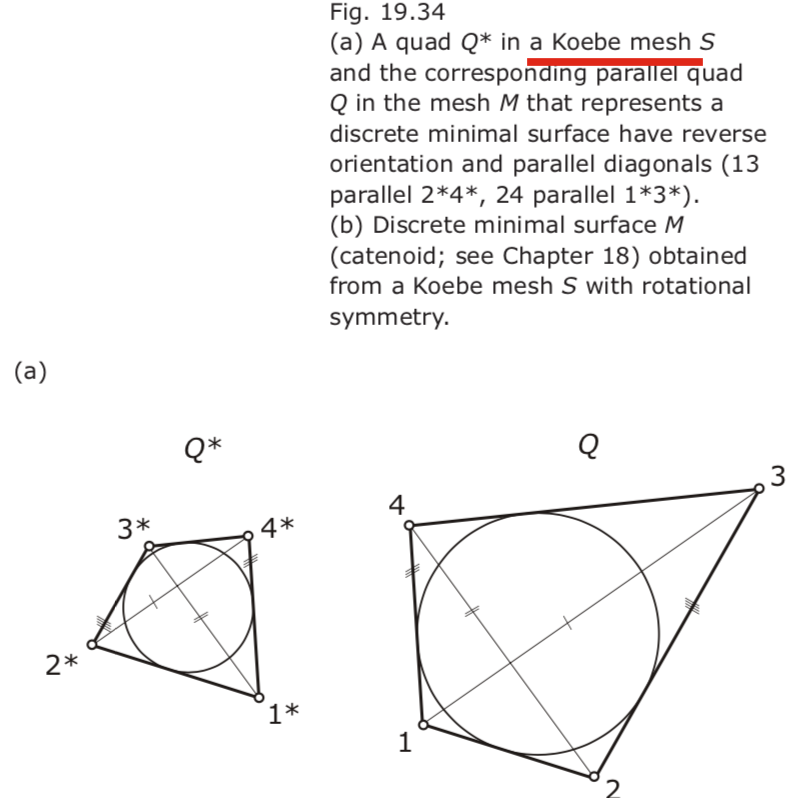
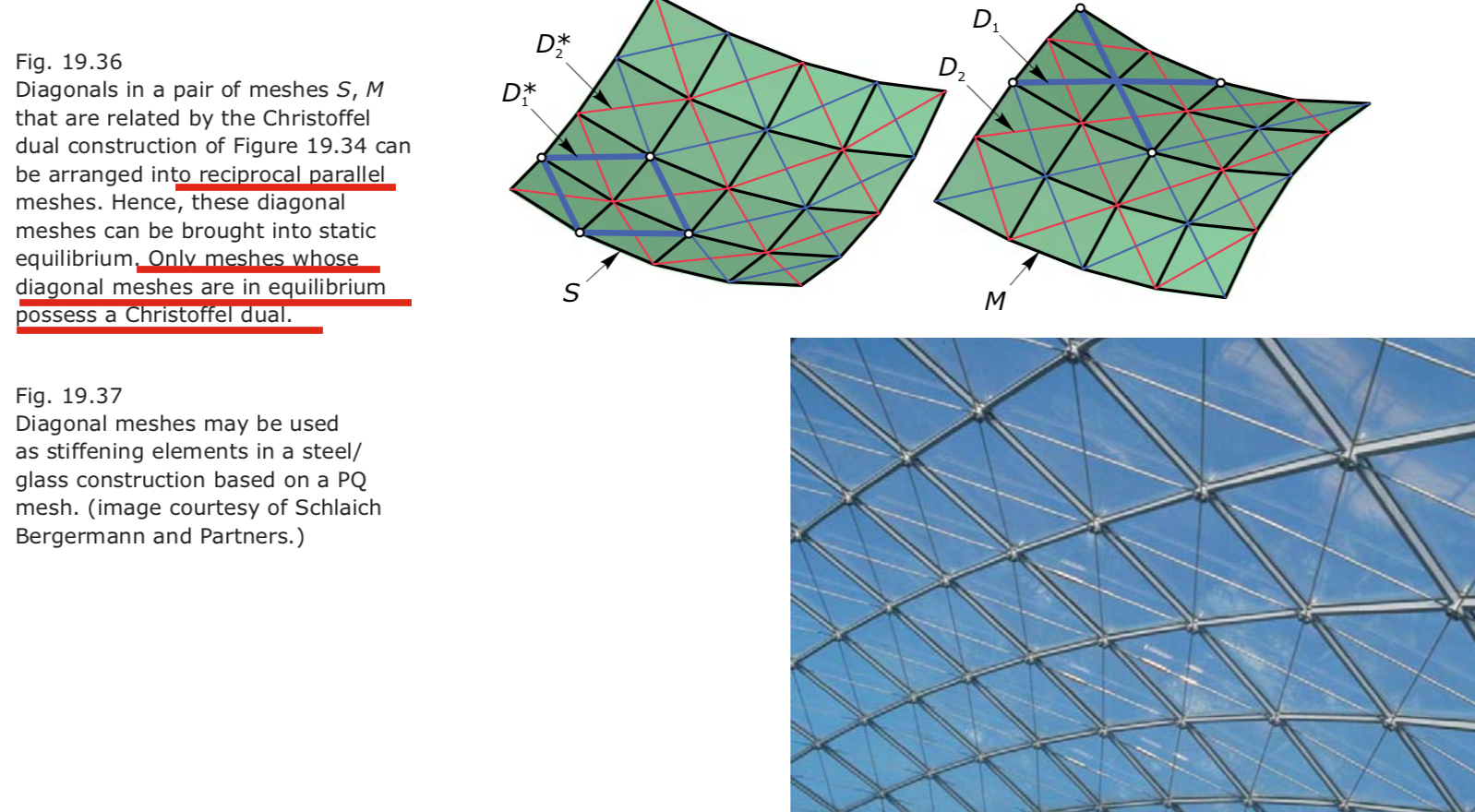
- The Christoffel dual: static equilibrium of diagonal meshes. M the Christoffel dual of S.

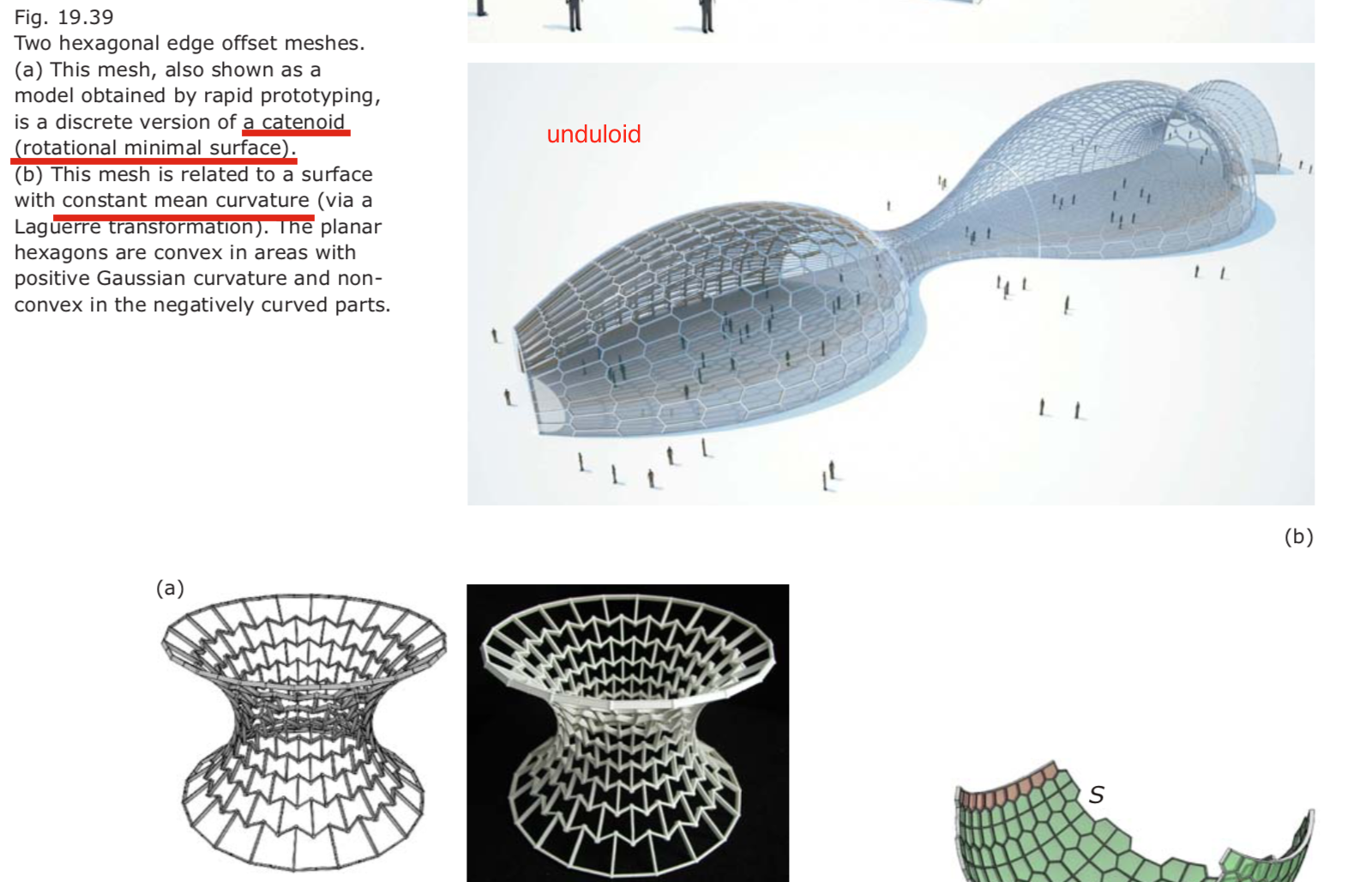
- Beyond quad meshes.